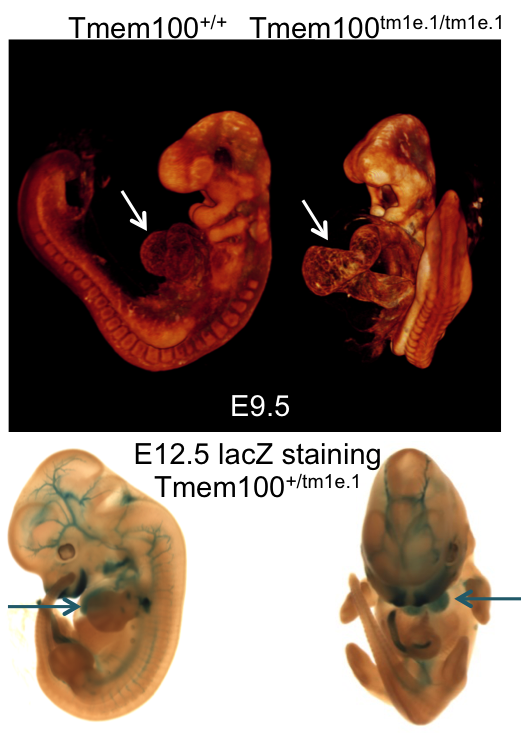
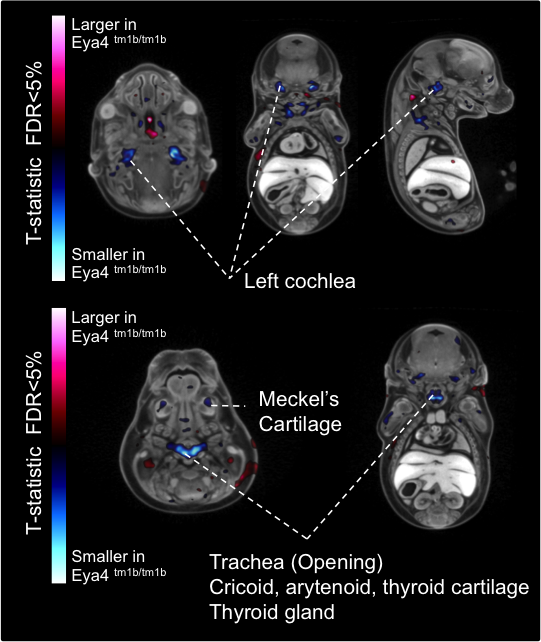
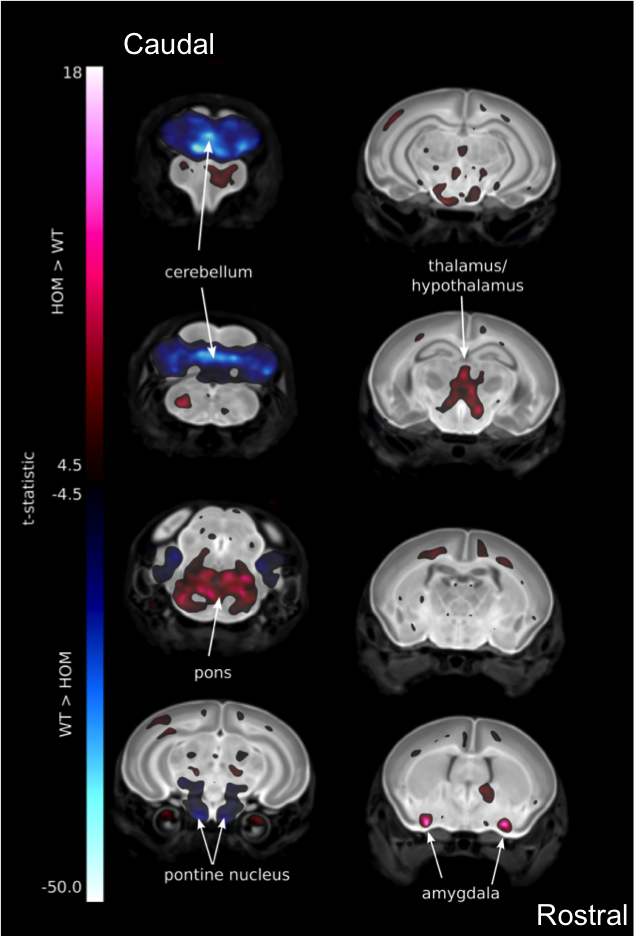
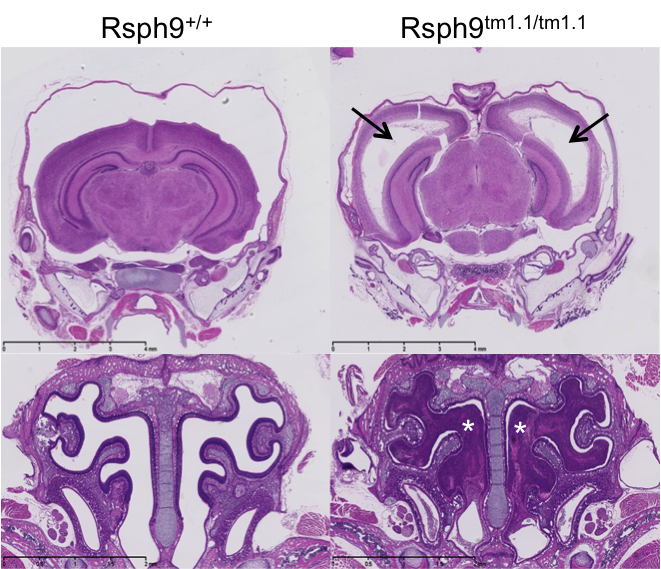
Introduction to IMPC Embryo Data
Up to one third of homozygous knockout lines are lethal, which means no homozygous mice or less than expected are observed past the weaning stage (IMPC Viability Primary Screen procedure). Early death may occur during embryonic development or soon after birth, during the pre-weaning stage. For this reason, the IMPC established a systematic embryonic phenotyping pipeline to morphologically evaluate mutant embryos to ascertain the primary perturbations that cause early death and thus gain insight into gene function.
As determined in IMPReSS (see interactive diagram here), all embryonic lethal lines undergo gross morphology assessment at E12.5 (embryonic day 12.5) to determine whether defects occur earlier or later during embryonic development. A comprehensive imaging platform is then used to assess dysmorphology. Embryo gross morphology, as well as 2D and 3D imaging are actively being implemented by the IMPC for lethal lines.
Read more in our paper on High-throughput discovery of novel developmental phenotypes, Nature 2016.
Accessing Embryo Phenotype Data
Embryo phenotype data can be accessed in multiple ways:
- Embryo Images: interactive heatmap A compilation of all our Embryo Images, organised by gene and life stage, with access to the Interactive Embryo Viewer, where you can compare mutants and wild types side by side and rotate 2D and 3D images; we also provide access to our external partners' embryo images.
- Embryo Vignettes Showcase of best embryo images with detailed explanations.
- From the FTP site, latest release All our results. Reports need to be filtered by a dedicated column, Life Stage (E9.5, E12.5, E15.5 and E18.5). Please check the README file or see documentation here.
- Using the REST API (see documentation here)
Determining Lethal Lines
The IMPC assesses each gene knockout line for viability (Viability Primary Screen IMPC_VIA_001). In this procedure, the proportion of homozygous pups is determined soon after birth, during the preweaning stage, in litters produced from mating heterozygous animals. A line is declared lethal if no homozygous pups for the null allele are detected at weaning age, and subviable if pups homozygous for the null allele constitute less than 12.5% of the litter.
Lethal strains are further phenotyped in the embryonic phenotyping pipeline. For embryonic lethal and subviable strains, heterozygotes are phenotyped in the IMPC adult phenotyping pipeline.
IMPC Embryo Phenotyping - Goals and Procedures
With up to one third of knockout strains being embryonic lethal, a systematic unbaised phenotyping pipeline was established to perform morphologic and imaging evaluation of mutant embryos to define the primary perturbations that cause their death. From this important insights are gained into gene function.
IMPC centers funded by the NIH Common fund mechanism are delivering the following for All Lines:
- Viability
- Heterozygote E12.5 Embryonic LacZ staining ( 2 mutant animals, wt reference images)
For All Embryonic Lethal Lines, gross morphology is assessed at E12.5 to determine if defects occur earlier or later in development. A comprehensive imaging platform is then used to assess dysmorphology at the most appropriate stage:
| Procedure | Number | Note |
|---|---|---|
| E9.5 Gross morphology | at least 2 homs,2 wt | images optional |
| E9.5 OPT screening | at least 2 homs | reconstructions available |
| E14.5-E15.5 Gross morphology | at least 2 homs, 2 wt | images optional |
| E14.5-E15.5 microCT screening | at least 2 homs | reconstructions available |
| E14.5 HREM | at least 3 homs, 1wt | reconstructions available |
| E18.5 Gross morphology | at least 2 homs | images optional |
| E18.5 microCT | at least 2 homs, 2 wt | reconstructions available |
In addition, the NIH is supporting in-depth phenotyping of embryonic lethal lines with three current awardees.
Trevor William, University of Colorado School of Medicine
Jesse Mager, University of Massachusetts Amherst
2D Imaging
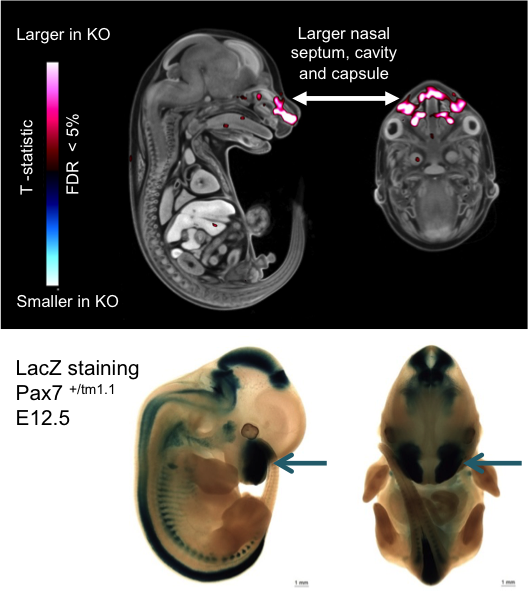
Embryo LacZ
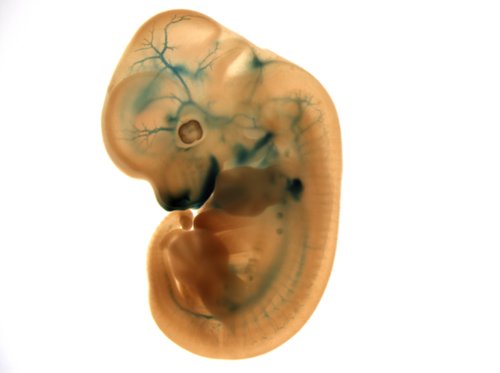
The majority of IMPC knockout strains replace a critical protein coding exon with a LacZ gene expression reporter element. Heterozygote E12.5 embryos from IMPC strains are treated to determine in situ expression of the targeted gene.
See all genes with embryo LacZ images.
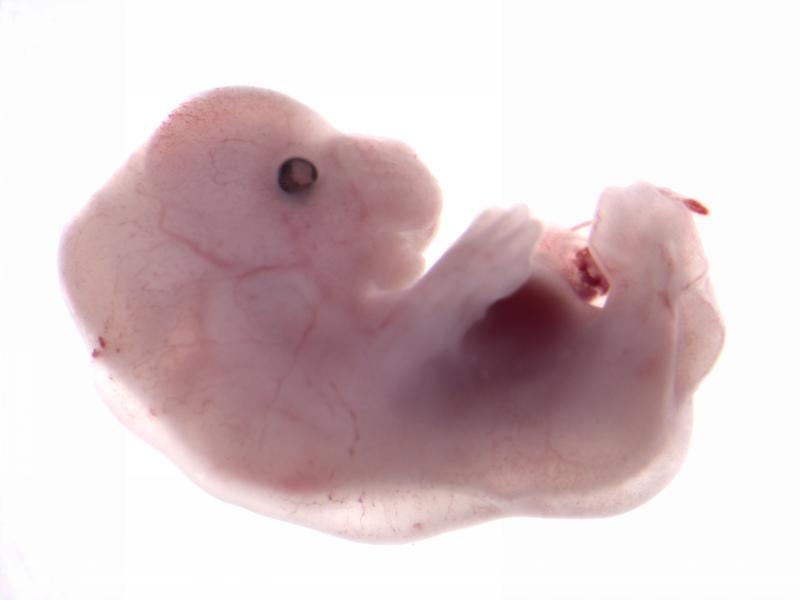
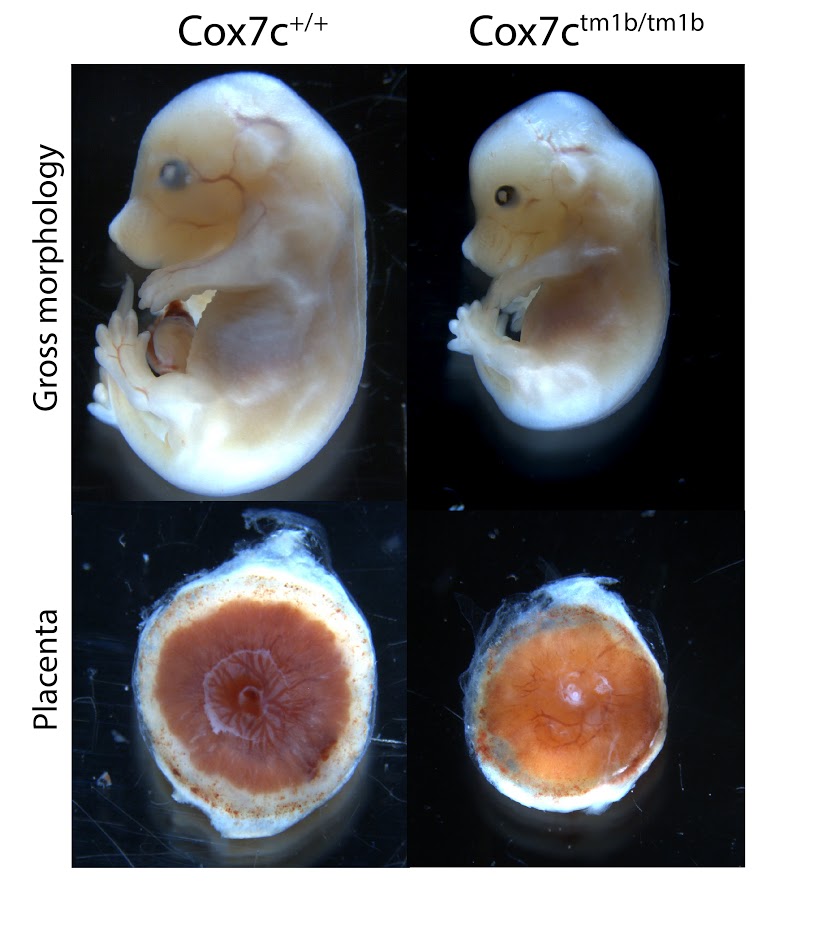
Embryo Gross Morphology
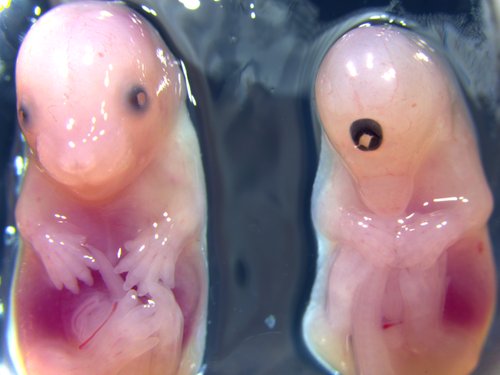
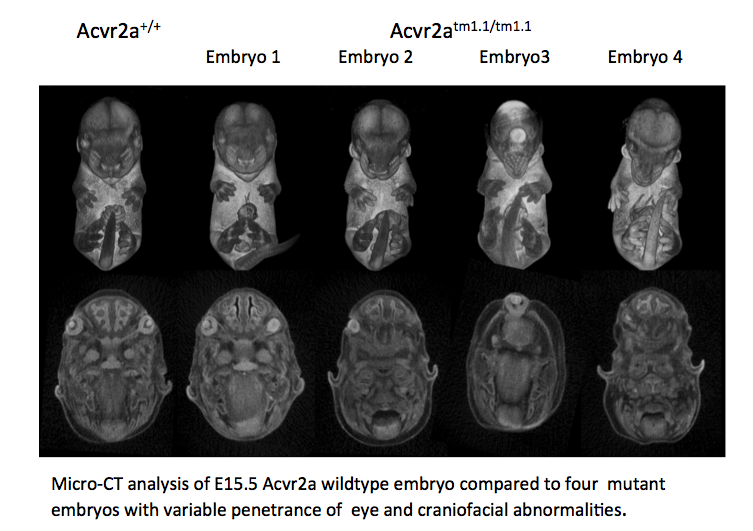
WT / Acvr2a
Gross morphology of embryos from lethal and subviable strains highlights which biological systems are impacted when the function of a gene is turned off. The developmental stage selected is determined by an initial assessment.
See embryo gross morphology images for E12.5, E14.5-E15.5, E18.5.
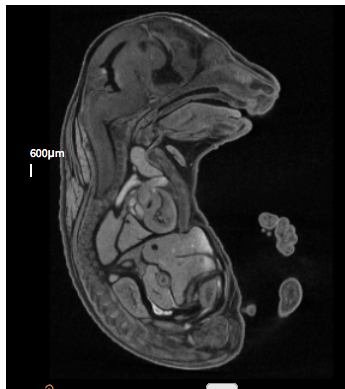
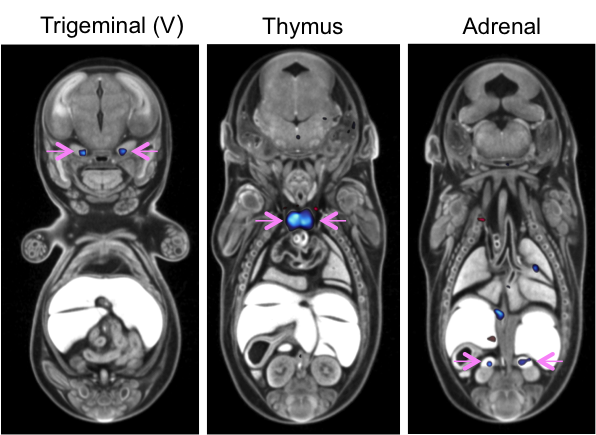
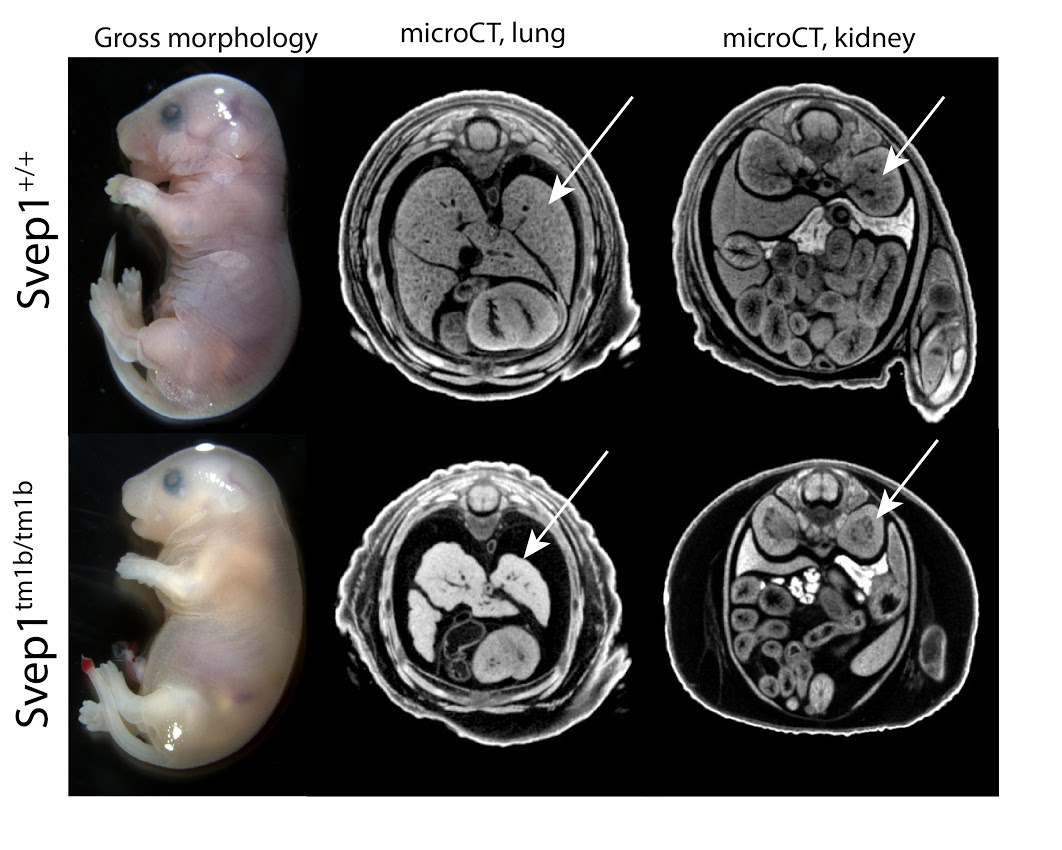
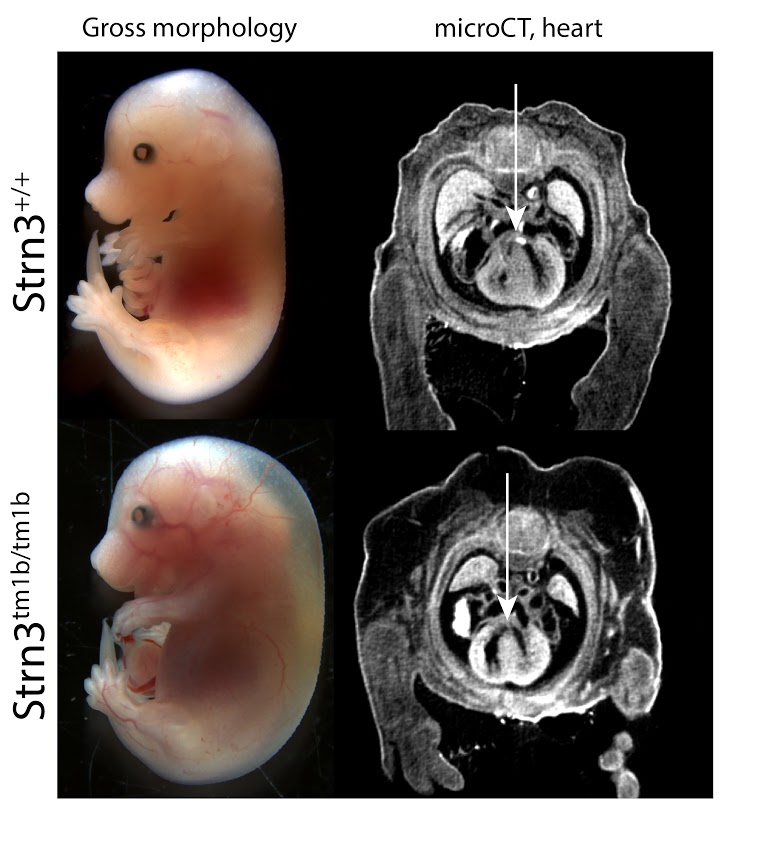
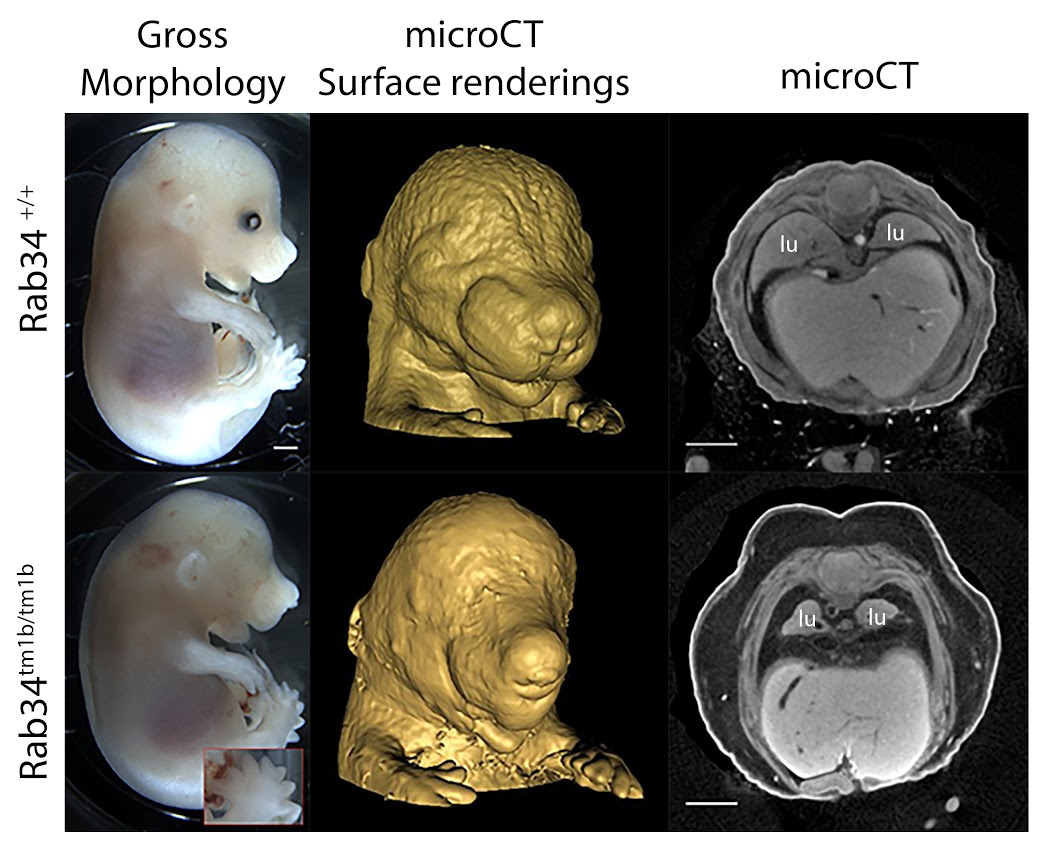
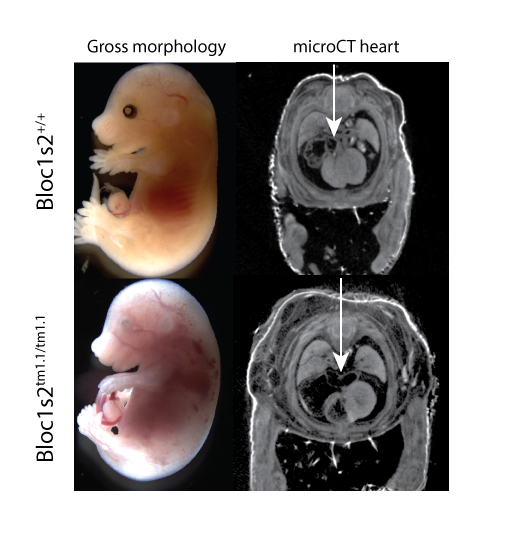
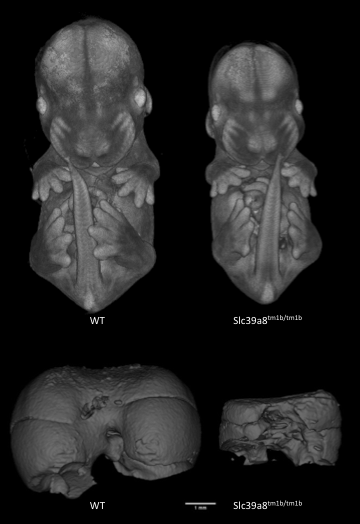
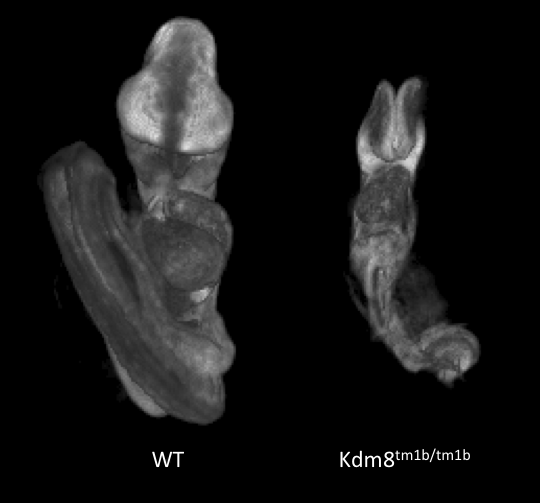
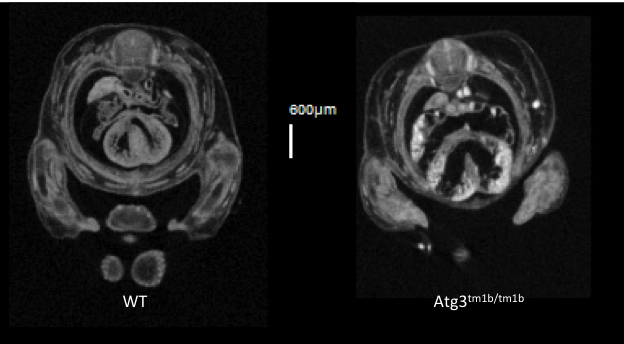
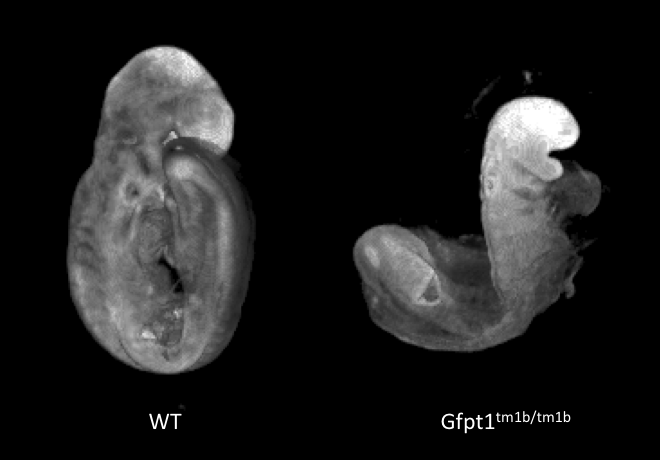
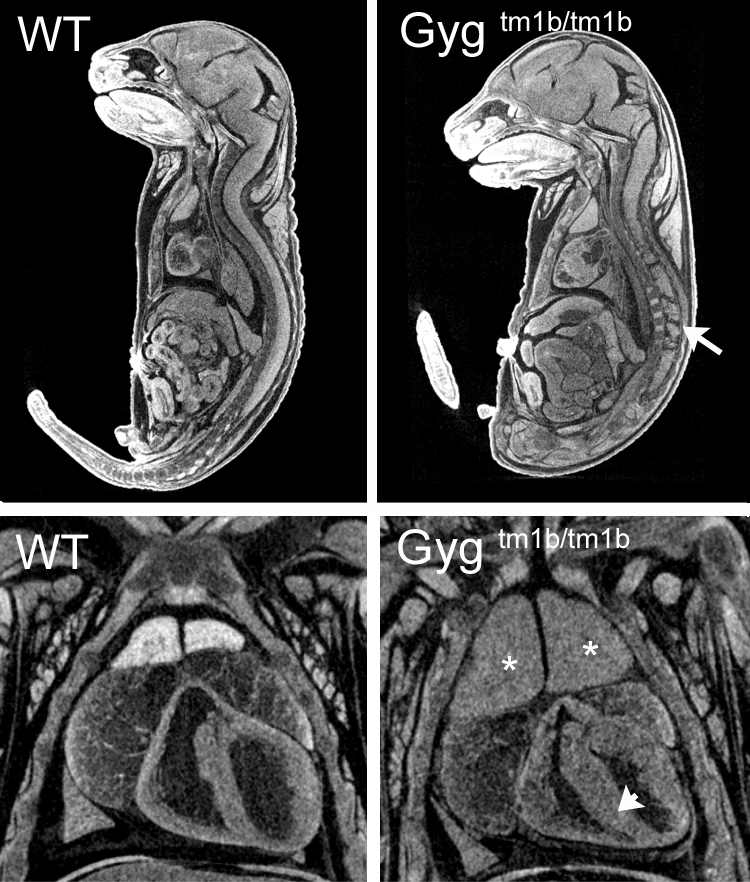
3D Imaging
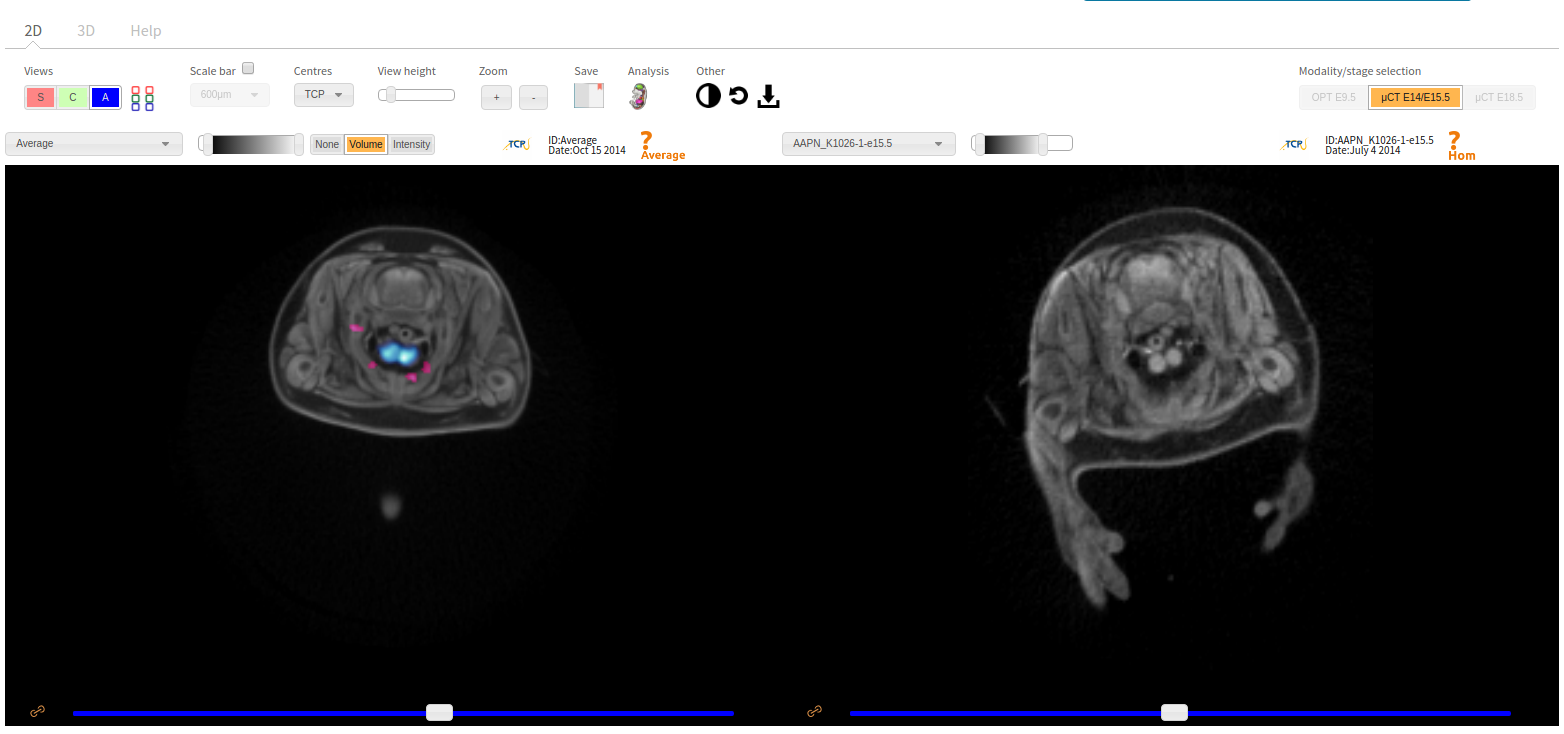
The embryonic and perinatal lethal pipeline comprises several 3D imaging modalities to quantify aberrant morphology that could not be determined by gross inspection. Images acquired by micro-CT and OPT are available via our Interactive Embryo Viewer (IEV).
Vignettes
These vignettes highlight the utility of embryo phenotyping pipeline and demonstrate how gross morphology, embryonic lacz expression, and high resolution 3D imaging provide insights into developmental biology. Clicking on an image will provide more information.